Python allows you to handle complex string formatting efficiently with the help of the format() function. You can put placeholders defined by a pair of curly braces in a string. Call the string.format() function and pass the value you want to put into the placeholders as parameters.
Given below are a few examples of string formatting in Python.
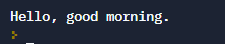
myString = 'Hello, good {}.'.format('morning')
print(myString)
We can use the placeholders multiple times in a string. Make sure you pass all the parameters in the format() function.
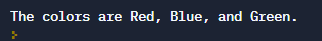
myString = 'The colors are {}, {}, and {}.'.format('Red','Blue','Green')
print(myString)
While using the format() function, we can insert values into the string by using index-based positions.
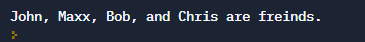
myString = 'John, {0}, {1}, and {2} are freinds.'.format('Maxx','Bob','Chris')
print(myString)
myString = 'John, {2}, {1}, and {0} are freinds.'.format('Maxx','Bob','Chris')
print(myString)

We can also reuse the parameters of the format() function inside the string.
myString = 'John, {0}, {1}, and {0} are freinds.'.format('Maxx','Bob')
print(myString)

myString = "{0}{1}{0}".format("abra","cad")
print(myString)

We can also insert values into the string by using assigned keywords for the parameters in the format() function.
myString = "The teams qualified for Champions League final are {finalist_1} and {finalist_2} ".format(finalist_1="Real Madrid",finalist_2="FC Barcelona")
print(myString)

fruits=['apple','orange','mango']
myString = "The fruits inside the bucket are {0}, {1} and {2}.".format(fruits[0],fruits[1],fruits[2])
print(myString)

myString = "{language} programming is fun.\n{language} is easy to learn.".format(language="Python")
print(myString)

By using string formatting, you can combine non-strings with strings.
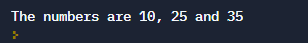
myString = "The numbers are {}, {} and {}".format(10,25,35)
print(myString)
Recent Posts
Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules. In this tutorial, let's understand what modular...
While Flask provides the essentials to get a web application up and running, it doesn't force anything upon the developer. This means that many features aren't included in the core framework....

